

Since then, there have been several extensions to the SIMD instruction sets for both architectures. Intel responded in 1999 by introducing the all-new SSE system. This sparked the introduction of the much more powerful AltiVec system in the Motorola PowerPC's and IBM's POWER systems.
The first widely deployed desktop SIMD was with Intel's MMX extensions to the x86 architecture in 1996.
MIPS followed suit with their similar MDMX system. Sun Microsystems introduced SIMD integer instructions in its " VIS" instruction set extensions in 1995, in its UltraSPARC I microprocessor. Hewlett-Packard introduced MAX instructions into PA-RISC 1.1 desktops in 1994 to accelerate MPEG decoding. As desktop processors became powerful enough to support real-time gaming and audio/video processing during the 1990s, demand grew for this particular type of computing power, and microprocessor vendors turned to SIMD to meet the demand. The current era of SIMD processors grew out of the desktop-computer market rather than the supercomputer market. Supercomputing moved away from the SIMD approach when inexpensive scalar MIMD approaches based on commodity processors such as the Intel i860 XP became more powerful, and interest in SIMD waned. For example, each of 65,536 single-bit processors in a Thinking Machines CM-2 would execute the same instruction at the same time, allowing, for instance, to logically combine 65,536 pairs of bits at a time, using a hypercube-connected network or processor-dedicated RAM to find its operands. These computers had many limited-functionality processors that would work in parallel. The first era of modern SIMD computers was characterized by massively parallel processing-style supercomputers such as the Thinking Machines CM-1 and CM-2. Vector processing architectures are now considered separate from SIMD computers: Duncan's Taxonomy includes them where Flynn's Taxonomy does not, due to Flynn's work (1966, 1972) pre-dating the Cray-1 (1977). Vector processing was especially popularized by Cray in the 1970s and 1980s. SIMD was the basis for vector supercomputers of the early 1970s such as the CDC Star-100 and the Texas Instruments ASC, which could operate on a "vector" of data with a single instruction. The first use of SIMD instructions was in the ILLIAC IV, which was completed in 1966. SIMT is true simultaneous parallel hardware-level execution.
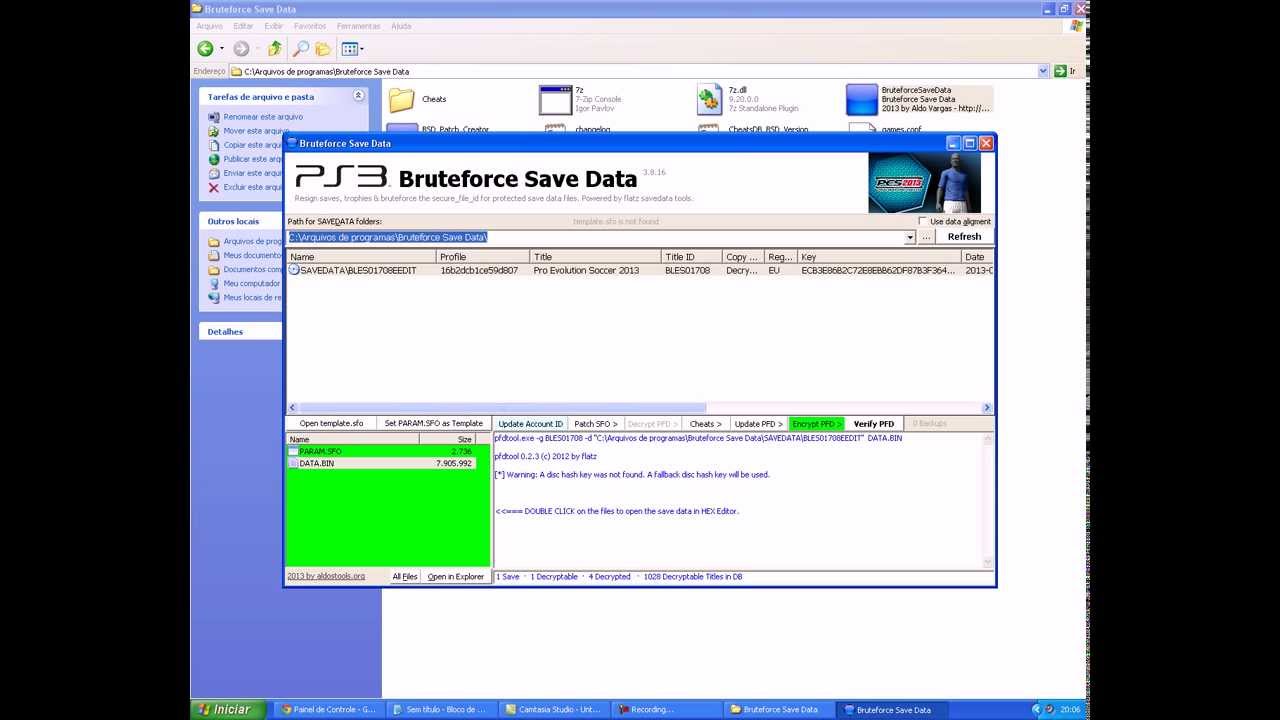
#Pes 2013 Multi Converter 1.4 With Pc software#
SIMT should not be confused with software threads or hardware threads, both of which are task time-sharing (time-slicing). SIMD has three different subcategories in Flynn's 1972 Taxonomy, one of which is SIMT.

Most modern CPU designs include SIMD instructions to improve the performance of multimedia use. SIMD is particularly applicable to common tasks such as adjusting the contrast in a digital image or adjusting the volume of digital audio. Such machines exploit data level parallelism, but not concurrency: there are simultaneous (parallel) computations, but each unit performs the exact same instruction at any given moment (just with different data). SIMD describes computers with multiple processing elements that perform the same operation on multiple data points simultaneously. SIMD can be internal (part of the hardware design) and it can be directly accessible through an instruction set architecture (ISA): it should not be confused with an ISA. Single instruction, multiple data ( SIMD) is a type of parallel processing in Flynn's taxonomy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
